Timeout example in Kogito Serverless Workflow
In the serverless-workflow-timeouts-showcase you can see an end-to-end example that contains a serverless workflow application with timeouts configured alongside Job Service running on Knative.
There are two workflows that showcase the timeouts usage in the Callback and Switch states.
Callback workflow
It is a simple workflow, where once the execution reaches the callback state it waits for the event callbackEvent to arrive and continue the execution.
{
"name": "callbackEvent",
"source": "",
"type": "callback_event_type"
}The timeout is configured with a maximum time 30 seconds to be waited by the workflow to receive the callbackEvent, in case it does not arrive in time, the execution moves, and the eventData variable remains null. See the callback state definition.
Switch workflow
The switch example is similar to the callback but once the execution reaches the state, it waits for one of the two configured events, visaDeniedEvent or visaApprovedEvent, to arrive, see the switch state definition.
If any of the configured events arrives before the timeout is overdue, the workflow execution moves to the next state defined in the corresponding transition.
If none of the events arrive before the timeout is overdue, the workflow then moves to the state defined in defaultCondition transition.
Event workflow
The event example is similar to the switch one but once the execution reaches the state, it waits for one of the configured events, event1 or event2, to arrive, see the event state definition.
If none of the configured events arrive before the timeout is overdue, the workflow execution moves to the next state defined in the corresponding transition property, skipping the events that were not received in time together with actions configured for them.
If one of the events arrives before the timeout is overdue, the workflow then moves to the state defined in transition, executing the corresponding event that has arrived in the state definition together with actions defined for it.
Running the example
To run the example you must have access to a kubernetes cluster running with Knative configured.
For simplicity, the example uses minikube, you can follow the steps described in the example’s readme.
|
All the descriptor files used to deploy the example infrastructure are present in the example. |
The database and Job Service deployment files are located under /kubernetes folder.
The descriptors related to the workflow application are generated after the build under /target/kubernetes.
The following diagram shows the example’s architecture when it is deployed in the Kubernetes + Knative infrastructure.
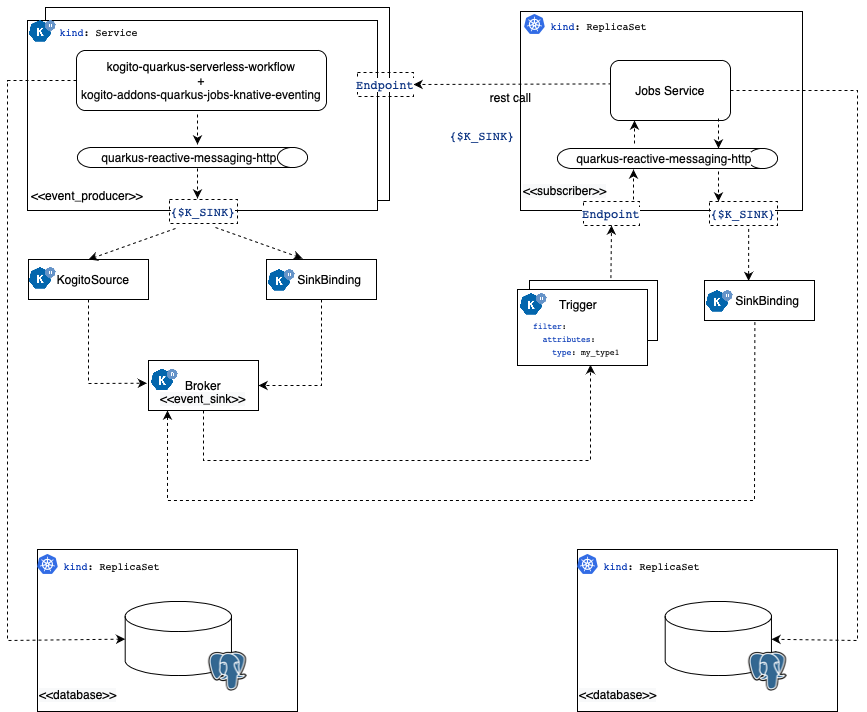
Deploying the database
The workflow application and Job Service uses PostgreSQL as the persistence backend to store information about the workflow instances and jobs, respectively. In the example you can deploy a single database instance to be used on both, in a production environment is recommended to have independent database instances.
To run PostgreSQL you need to apply the following on the cluster:
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/timeouts-showcase-database.ymlsecret/timeouts-showcase-database created
deployment.apps/timeouts-showcase-database created
service/timeouts-showcase-database createdDeploying Job Service
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/jobs-service-postgresql.ymlservice/jobs-service-postgresql created
deployment.apps/jobs-service-postgresql created
trigger.eventing.knative.dev/jobs-service-postgresql-create-job-trigger created
trigger.eventing.knative.dev/jobs-service-postgresql-cancel-job-trigger created
sinkbinding.sources.knative.dev/jobs-service-postgresql-sb createdDeploying the timeout showcase workflow
You need to build the workflow with the knative maven profile, then the descriptor files are generated under the target/kubernetes folder, and the image is pushed in the container registry.
mvn clean install -Pknativekubectl apply -f target/kubernetes/knative.yml
kubectl apply -f target/kubernetes/kogito.ymlservice.serving.knative.dev/timeouts-showcase created
trigger.eventing.knative.dev/visa-denied-event-type-trigger-timeouts-showcase created
trigger.eventing.knative.dev/visa-approved-event-type-trigger-timeouts-showcase created
trigger.eventing.knative.dev/callback-event-type-trigger-timeouts-showcase created
sinkbinding.sources.knative.dev/sb-timeouts-showcase createdCreating a workflow instance
To create a workflow you can interact with the workflow using the provided REST APIs, in the example provide a test Web UI to make it easy to test.
First, you need to get the service URL on the cluster.
kn service list | grep timeouts-showcaseNAME URL LATEST AGE CONDITIONS READY REASON
timeouts-showcase http://timeouts-showcase.default.10.105.86.217.sslip.io timeouts-showcase-00001 3m50s 3 OK / 3 TrueUsing the showcase UI
The example Web UI is handy to interact with the workflow, you just need to open in the browser the URL you got from the previous step.
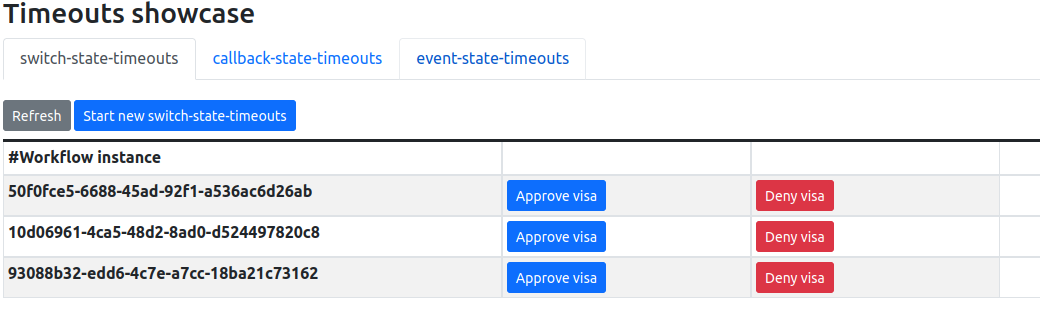
You can create new workflow instances and interact with them to complete, or simply wait for the timeout to be triggered to check it’s working. More details on the readme.
Using REST APIs
You can test the workflows using the REST APIs, in fact they are the same used by the Web UI in both workflows.
-
Callback
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://timeouts-showcase.default.10.105.86.217.sslip.io/callback_state_timeouts' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{}'-
Switch
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://timeouts-showcase.default.10.105.86.217.sslip.io/callback_state_timeouts' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{}'-
Event
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://timeouts-showcase.default.10.105.86.217.sslip.io/event_state_timeouts' \
-H 'accept: */*' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{}'-
Checking whether the workflow instance was created
curl -X 'GET' 'http://timeouts-showcase.default.10.105.86.217.sslip.io/switch_state_timeouts'The command will produce an output like this, which indicates that the process is waiting for an event to arrive.
[{"id":"2e8e1930-9bae-4d60-b364-6fbd61128f51","workflowdata":{}}]-
Checking the timeout was executed after 30 seconds:
curl -X 'GET' 'http://timeouts-showcase.default.10.105.86.217.sslip.io/switch_state_timeouts'
[]As you can see there are no active workflow instances, indicating the timeout was executed and the created instance was completed.
Found an issue?
If you find an issue or any misleading information, please feel free to report it here. We really appreciate it!