Data Index Core Concepts
In SonataFlow platform there is a dedicated supporting service that stores the data related to the workflow instances and their associated jobs called Data Index service. This service also provides a GraphQL endpoint allowing users to query that data and perform operations, also known as mutations in GraphQL terms.
The data processed by the Data Index service is usually received via events. The events consumed can be generated by any workflow or the Job service itself. This event communication can be configured in different ways as described in the Data Index communication configuration section.
The Data Index service uses Apache Kafka or Knative eventing to consume CloudEvents messages from workflows. The event data is indexed and stored in the database for querying via GraphQL. These events contain information about units of work executed for a workflow. The Data Index service is at the core of all SonataFlow search, insight, and management capabilities.
The SonataFlow Data Index Service has the following key attributes:
-
Flexible data structure
-
Distributable and cloud-ready format
-
Message-based communication with workflows (Apache Kafka, Knative, CloudEvents)
-
Powerful querying API using GraphQL
-
Management capabilities using the Gateway API, to perform actions using GraphQL syntax on remote runtimes with a single entrypoint
Data Index service in SonataFlow
The SonataFlow Data Index Service is a Quarkus application, based on Vert.x with Reactive Messaging, that exposes a GraphQL endpoint that client applications use to access indexed data and perform management operations related to running workflow instances.
|
The indexing functionality in the Data Index service is provided by choosing one of the following persistence providers: |
The Data Index Service has been thought of as an application to store and query the existing workflow data. The data comes contained in events. The service allows multiple connection options as described in the Data Index service communication configuration section.
Data Index scenarios
Data Index is distributed in different ways to allow deployment in different topologies, and depending on how the data is indexed.
The following sections describe the different options of Data Index deployments.
Data Index as a standalone service
It can be deployed explicitly referencing the image, starting a separated service inside a container. See Data Index standalone.
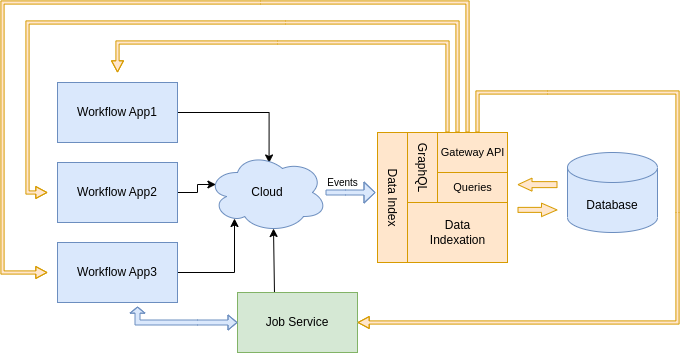
This type of deployment requires to choose the right image depending on the persistence, specify the database connection properties, and the event consumption configuration.
Data Index service as Quarkus Development service
It also can be deployed, transparently as a Quarkus Development Service when the Quarkus Dev mode is used in the SonataFlow application. When you use the SonataFlow Process Quarkus extension, a temporary Data Index Service is automatically provisioned while the Quarkus application is running in development mode and the Dev Service is set up for immediate use.
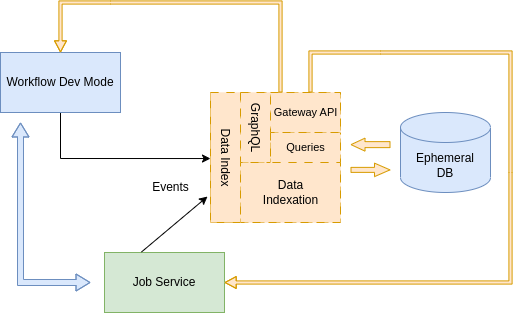
More details are provided in the Data Index as a Quarkus Development service section.
The SonataFlow Process Quarkus extension sets up your Quarkus application to automatically replicate any SonataFlow messaging events related to workflow instances or jobs into the provisioned Data Index instance.
For more information about Quarkus Dev Services, see Dev Services guide.
Data Index service as Quarkus extension
It can be included as part of the same SonataFlow application using the Data Index extension, through the provided addons.
This scenario is specific to add the Data Index data indexing features and the GraphQL endpoint exposure inside a workflow application.
The communication with the workflow where the extension is added, is something internal to the application, allowing to simplify the communication between services and avoiding extra configuration for that purpose.
In this case, the indexation has some limitations: it is only able to index data from the workflows deployed in the same application.
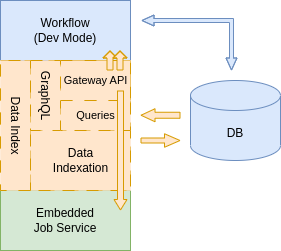
More details are available in the Data Index Quarkus Extension section.
Data Index storage
In order to store the indexed data, Data Index needs some specific tables to be created. Data Index is ready to use Quarkus flyway for that purpose.
It’s necessary to activate the migrate-at-start option to migrate the Data Index schema automatically.
For more details about Flyway migrations, see PostgreSQL Database Migration section
Data Index GraphQL endpoint
Data Index provides GraphQL endpoint that allows users to interact with the stored data. For more information about GraphQL see GraphQL
GraphQL queries for workflow instances and jobs
This guide provides as examples, some GraphQL queries that allow to retrieve data about workflow instances and jobs.
- Retrieve data from workflow instances
-
You can retrieve data about a specified instance from your workflow definition.
Example query{ ProcessInstances { id processId state parentProcessInstanceId rootProcessId rootProcessInstanceId variables nodes { id name type } } } - Retrieve data from jobs
-
You can retrieve data from a specified job instance.
Example query{ Jobs { id status priority processId processInstanceId executionCounter } } - Filter query results using the
whereparameter -
You can use the
whereparameter with multiple combinations to filter query results based on workflow attributes.Example query{ ProcessInstances(where: {state: {equal: ACTIVE}}) { id processId processName start state variables } }Example query{ ProcessInstances(where: {id: {equal: "d43a56b6-fb11-4066-b689-d70386b9a375"}}) { id processId processName start state variables } }By default, all filtered attributes are executed as
ANDoperations in queries. You can modify this behavior by combining filters with anANDorORoperator.Example query{ ProcessInstances(where: {or: {state: {equal: ACTIVE}, rootProcessId: {isNull: false}}}) { id processId processName start end state } }Example query{ ProcessInstances(where: {and: {processId: {equal: "travels"}, or: {state: {equal: ACTIVE}, rootProcessId: {isNull: false}}}}) { id processId processName start end state } }Depending on the attribute type, the following operators are also available:
-
String array argument:
-
contains: String -
containsAll: Array of strings -
containsAny: Array of strings -
isNull: Boolean (trueorfalse)
-
-
String argument:
-
in: Array of strings -
like: String -
isNull: Boolean (trueorfalse) -
equal: String
-
-
ID argument:
-
in: Array of strings -
equal: String -
isNull: Boolean (trueorfalse)
-
-
Boolean argument:
-
isNull: Boolean (trueorfalse) -
equal: Boolean (trueorfalse)
-
-
Numeric argument:
-
in: Array of integers -
isNull: Boolean -
equal: Integer -
greaterThan: Integer -
greaterThanEqual: Integer -
lessThan: Integer -
lessThanEqual: Integer -
between: Numeric range -
from: Integer -
to: Integer
-
-
Date argument:
-
isNull: Boolean (trueorfalse) -
equal: Date time -
greaterThan: Date time -
greaterThanEqual: Date time -
lessThan: Date time -
lessThanEqual: Date time -
between: Date range -
from: Date time -
to: Date time
-
-
- Sort query results using the
orderByparameter -
You can use the
orderByparameter to sort query results based on workflow attributes. You can also specify the direction of sorting in ascendingASCorder or descendingDESCorder. Multiple attributes are applied to the database query in the order they are specified in the query filter.Example query{ ProcessInstances(where: {state: {equal: ACTIVE}}, orderBy: {start: ASC}) { id processId processName start end state } } - Limit and offset query results using the
paginationparameter -
You can use the
paginationparameter to specify alimitandoffsetfor query results.Example query{ ProcessInstances(where: {state: {equal: ACTIVE}}, orderBy: {start: ASC}, pagination: {limit: 10, offset: 0}) { id processId processName start end state } }
Data Index service Gateway API
Data Index incorporates a set of queries or mutations that allow firing operations on workflow endpoints using GraphQL notation.
The Data Index Gateway API enables you to perform the following operations:
- Abort a workflow instance
-
Retrieves a workflow instance with the ID passed as a parameter and launches the abort operation on related SonataFlow service.
Example mutation for abort operationmutation { ProcessInstanceAbort (id:"66e05e9c-eaab-47af-a83e-156498b7096d") } - Retry a workflow instance
-
Retrieves a workflow instance with the id passed as a parameter and launches the retry operation on related SonataFlow service.
Example mutation for retry operationmutation { ProcessInstanceRetry (id:"66e05e9c-eaab-47af-a83e-156498b7096d") } - Skip a workflow instance
-
Retrieves a workflow instance with the ID passed as a parameter and launches the skip operation on related SonataFlow service.
Example mutation for skip operationmutation { ProcessInstanceSkip (id:"66e05e9c-eaab-47af-a83e-156498b7096d") } - Retrieve workflow instance nodes
-
Retrieves the nodes of a workflow instance that are coming from the process definition. When the
nodeDefinitionsfield of a workflow instance is queried, a call to a specific SonataFlow service is generated to retrieve the requested list of available nodes.Example query to retrieve workflow instance nodes{ProcessInstances(where: { id: {equal: "1017afb1-5749-440e-8b9b-6b876bb5894d"}}){ diagram }} - Update workflow instance variables
-
Updates the variables of a workflow instance using the
idpassed as a parameter. Retrieves a workflow instance using theidpassed as a parameter and launches the update operation on related SonataFlow service with the new values passed invariablesparameter.Example mutation to update workflow instance variablesmutation { ProcessInstanceUpdateVariables (id:"23147fcc-da82-43a2-a577-7a36b26094bd", variables:"{\"it_approval\":true,\"candidate\":{\"name\":\"Joe\",\"email\":\"jdoe@ts.com\",\"salary\":30000,\"skills\":\"java\"},\"hr_approval\":true}") } - Trigger a node instance
-
Triggers a node instance using the node definition
nodeId. ThenodeIdis included in thenodeInstancesof a workflow instance using theidpassed as parameter.Example mutation to trigger a node instancemutation{ NodeInstanceTrigger( id: "9674e3ed-8c13-4c3f-870e-7465d9ca7ca7", nodeId:"_B8C4F63C-81AD-4291-9C1B-84967277EEF6") } - Retrigger a node instance
-
Retriggers a node instance using the
id, which is similar tonodeInstanceIdrelated to a workflow instance. Theidof the workflow instance is passed as a parameter.Example mutation to retrigger a node instancemutation{ NodeInstanceRetrigger( id: "9674e3ed-8c13-4c3f-870e-7465d9ca7ca7", nodeInstanceId:"01756ba2-ac16-4cf1-9d74-154ae8f2df21") } - Cancel a node instance
-
Cancels a node instance with the
id, which is similar tonodeInstanceIdrelated to a workflow instance. Theidof the workflow instance is passed as a parameter.Example mutation to cancel a node instancemutation{ NodeInstanceCancel( id: "9674e3ed-8c13-4c3f-870e-7465d9ca7ca7", nodeInstanceId:"01756ba2-ac16-4cf1-9d74-154ae8f2df21") }To enable described management operations on workflow instances, make sure your project is configured to have the
kogito-addons-quarkus-process-managementdependency on itspom.xmlfile to have this management operations enabled, like:<dependency> <groupId>org.kie.kogito</groupId> <artifactId>kogito-addons-quarkus-process-management</artifactId> </dependency> - Retrieve the workflow instance source file content
-
Retrieves the workflow instance source file. When the
sourcefield of a workflow instance is queried, a call to a specific SonataFlow service is generated to retrieve the requested workflow instance source file content.Example query to retrieve a workflow instance source file content{ProcessInstances(where: { id: {equal: "1017afb1-5749-440e-8b9b-6b876bb5894d"}}){ source }}The workflow instance source field only will be available when
kogito-addons-quarkus-source-filesdependency is added on SonataFlow runtime servicepom.xmlfile.<dependency> <groupId>org.kie.kogito</groupId> <artifactId>kogito-addons-quarkus-source-files</artifactId> </dependency> - Reschedule a job
-
Reschedules a job using the
id. The jobidand other information are passed in thedataparameter.Example mutation to reschedule a jobmutation{ JobReschedule( id: "9674e3ed-8c13-4c3f-870e-7465d9ca7ca7", data:"{\"expirationTime\": \"2033-06-27T04:35:54.631Z\",\"retries\": 2}") } - Cancel a job
-
Cancels a job using the
idpassed as a parameter.Example mutation to cancel a jobmutation{ JobCancel( id: "9674e3ed-8c13-4c3f-870e-7465d9ca7ca7") }
Data Index GraphQL UI
Data Index GraphQL UI is provided to interact with GraphQL endpoint.
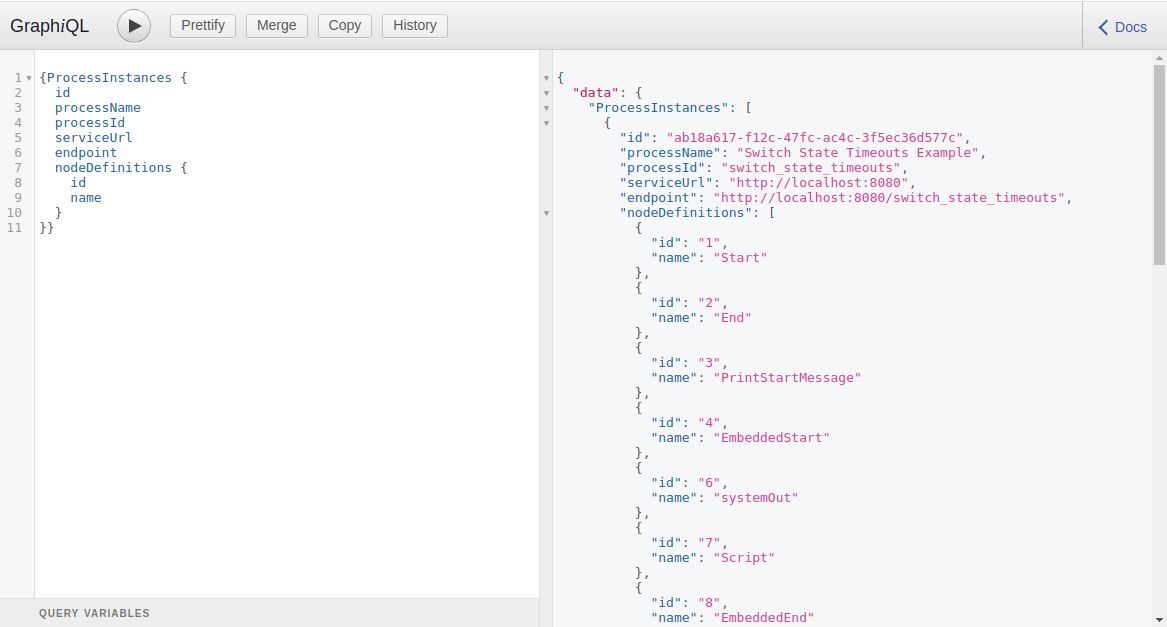
When the Data Index is deployed as a standalone service, this UI will be available at /graphiql/ endpoint (i.e: at http://localhost:8180/graphiql/)
To have the GraphQL UI available when the Data Index extension is deployed the property quarkus.kogito.data-index.graphql.ui.always-include needs to be enabled.
It will be accessible at: <quarkus.http.root-path><quarkus.http.non-application-root-path>/graphql-ui/ (i.e: http://localhost:8080/q/graphql-ui/)
|
The |
Data Index service communication configuration
In order to index the data, Data Index allows multiple connection options to be able to consume the information provided by the different workflows.
The final goal is to receive the application-generated data related to the workflow instances and jobs. The information that comes inside events, is indexed and stored in the database allowing it to be consumed through the provided GraphQL endpoint.
Knative Eventing
In order to interact with the Data Index separated service, use the Knative eventing system eventing:
-
Add the Data Index service and deployment, defining the Database connection properties and setting the
KOGITO_DATA_INDEX_QUARKUS_PROFILEtohttp-events-support. -
Specify the Knative Triggers to filter the Data Index events.
DataIndex resource with triggers definition (requires Knative):apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: data-index-service-postgresql-processes-trigger
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: ProcessInstanceEvent
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: data-index-service-postgresql
uri: /processes
---
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: data-index-service-postgresql-jobs-trigger
spec:
broker: default
filter:
attributes:
type: JobEvent
subscriber:
ref:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: data-index-service-postgresql
uri: /jobs-
Configure the workflow to use the K_SINK as outgoing connection url
application.properties file to communicate with Knativemp.messaging.outgoing.kogito-processinstances-events.connector=quarkus-http
mp.messaging.outgoing.kogito-processinstances-events.url=${K_SINK}
mp.messaging.outgoing.kogito-processinstances-events.method=POST|
Job service needs also to be configured to send the events to the Knative K_SINK to have them available for Data Index related triggers. |
Kafka eventing
To configure the communication between the Data Index Service and the workflow through Kafka, you must provide a set of configurations.
-
Add the Data Index service and deployment, defining the Database connection properties and setting the
KOGITO_DATA_INDEX_QUARKUS_PROFILEtokafka-events-support(this value is set by default). -
Configure the SonataFlow application to use the smallrye-kafka connector and the expected topic.
application.properties file to communicate with Kafkamp.messaging.outgoing.kogito-processinstances-events.connector=smallrye-kafka
mp.messaging.outgoing.kogito-processinstances-events.topic=kogito-processinstances-events
mp.messaging.outgoing.kogito-processinstances-events.value.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer|
Job service is configured to send the JobEvents to the kafka topic |
Found an issue?
If you find an issue or any misleading information, please feel free to report it here. We really appreciate it!